Dot dash line MATLAB empowers data visualization, allowing you to highlight specific data points and compare datasets effectively. This guide delves into the syntax, customization options, and various applications of dot-dash lines within MATLAB plots. We’ll explore how to create compelling visualizations that enhance data comprehension, from simple plots to complex scenarios involving multiple datasets and subplots.
Understanding the nuances of dot-dash line styles in MATLAB is crucial for effective data presentation. This tutorial provides a comprehensive overview, covering everything from basic plot creation to advanced customization techniques. The examples and explanations are designed to help you easily incorporate these techniques into your own projects.
Introduction to Dot-Dash-Line Plotting in MATLAB
Dot-dash line plots in MATLAB offer a visually distinct way to represent data, aiding in clear identification and comparison within graphs. This style, a combination of dots and dashes, provides a unique visual signature, making it particularly useful when multiple datasets are plotted on the same graph. This detailed guide will explore the creation and customization of dot-dash lines, offering practical examples and a comprehensive comparison with other line styles.Dot-dash lines in MATLAB are easily implemented, offering flexibility in customizing the appearance of plots.
Dot-dash line plotting in MATLAB is a super handy tool for visualizing data, and it’s a great way to create custom plots. Speaking of cool visuals, have you seen the photo of Victor Wembanyama browsing for Pokémon and Magic: The Gathering cards at a local shop? Here’s the photo. It’s definitely a fun break from the usual sports-related stuff.
Regardless, understanding how to create different types of lines, like dot-dash, in MATLAB is super useful for representing trends and patterns in data.
This flexibility is key to effectively conveying information and facilitating data analysis. Understanding the syntax and customization options is crucial for creating professional and informative visualizations.
Dot-Dash Line Syntax and Examples
Dot-dash lines are created in MATLAB using the `plot` function with the appropriate line style string. The syntax is straightforward and directly applicable.
`plot(x, y, ‘.-‘)`
Working with dot-dash lines in MATLAB can be tricky, but mastering them is key for visualizing data effectively. This is especially true when you’re analyzing complex datasets, like, say, the Ravens’ updated depth chart after Dalvin Cook signed a contract ahead of the NFL playoffs. This article highlights the impact of the signing on the team’s projected performance, which, in turn, can be visualized using specific dot-dash line configurations in MATLAB to compare projected outcomes.
Ultimately, understanding dot-dash lines in MATLAB is a valuable skill for any data analyst.
This command generates a dot-dash line plot using the x and y coordinates of the data points.Examples of dot-dash line plots using different data sets showcase the versatility of this plotting style.“`matlab% Example 1x = 1:10;y = x.^2;plot(x, y, ‘.-r’); % Red dot-dash line% Example 2x = linspace(0, 2*pi, 100);y = sin(x);plot(x, y, ‘.-g’); % Green dot-dash linehold on;plot(x, cos(x), ‘.-b’); % Blue dot-dash linehold off;“`These examples demonstrate how to plot data with varying line colors (red and green).
The `hold on` and `hold off` commands enable plotting multiple lines on the same graph. The second example illustrates the flexibility in plotting functions and using different colors to distinguish between different sets of data.
Customizing Dot-Dash Lines
The appearance of dot-dash lines can be further customized to enhance readability and visual appeal.
- Color: Various color specifications can be used within the `plot` command to change the color of the dot-dash line. For instance, ‘r’ for red, ‘b’ for blue, or color names like ‘magenta’ or ‘cyan’.
- Line Width: The width of the dot-dash line can be adjusted using the `LineWidth` property. A larger value corresponds to a thicker line. For example, `plot(x, y, ‘.-r’, ‘LineWidth’, 2)` will create a thicker red dot-dash line.
- Markers: You can add markers to the data points along the dot-dash line to highlight individual data points. For example, `plot(x, y, ‘.-or’)` will create a red dot-dash line with circular markers at each data point. Different marker types are available to suit your needs, including circles (‘o’), squares (‘s’), and stars (‘*’).
Comparison of Line Styles, Dot dash line matlab
The following table compares various line styles, including dot-dash, in MATLAB plots.
| Line Style | MATLAB Syntax | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid | ‘-‘ | A continuous line | plot(x,y,’-‘) |
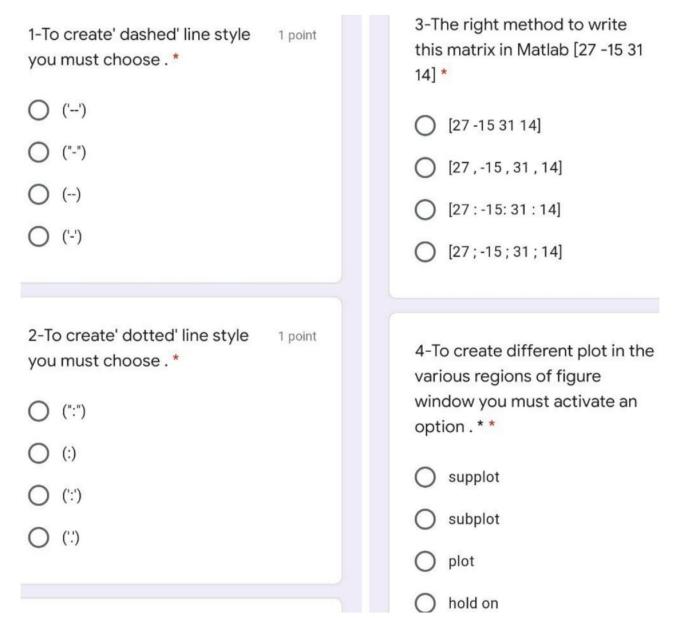
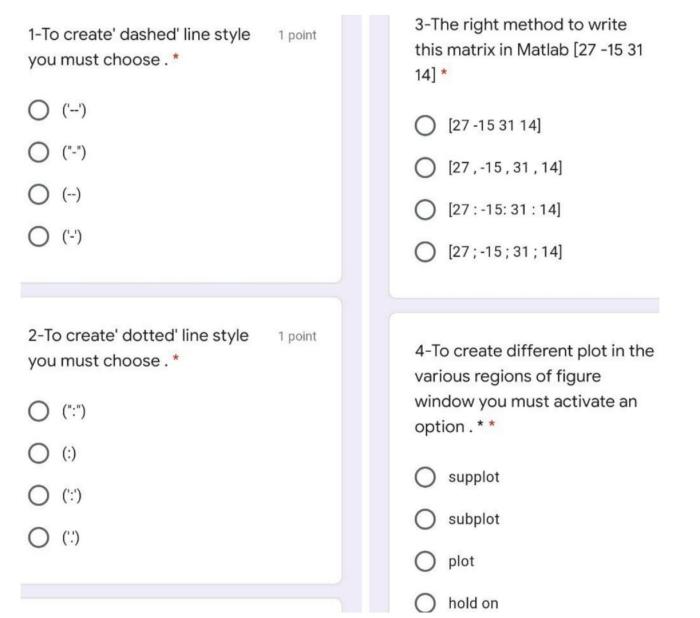
| Dashed | ‘–‘ | A dashed line | plot(x,y,’–‘) |
| Dotted | ‘:’ | A dotted line | plot(x,y,’:’) |
| Dash-dot | ‘-.’ | A combination of dashes and dots | plot(x,y,’-.’) |
| Dot-dash | ‘.-‘ | Combination of dots and dashes | plot(x,y,’.-‘) |
Dot-Dash Line Plots for Data Visualization
Dot-dash lines offer a unique way to highlight specific data points within a plot, enhancing clarity and distinguishing key trends. This approach is particularly useful when visualizing multiple datasets or complex patterns, enabling viewers to quickly identify crucial information. The strategic use of line styles is vital for effective data visualization, as it significantly impacts how the data is perceived and interpreted.
Highlighting Data Points with Dot-Dash Lines
Dot-dash lines effectively accentuate specific data points in a plot, making them stand out from the general trend. This is achieved by using the distinctive pattern of dots and dashes to draw attention to particular data values. For example, if one wishes to highlight significant experimental results or specific milestones in a time-series analysis, dot-dash lines can effectively focus attention on those data points.
Importance of Choosing Appropriate Line Styles
Choosing the right line style is crucial for effective data visualization. Different line styles convey distinct information and interpretations. A solid line generally represents a continuous trend, while a dashed line can indicate a discontinuous relationship or emphasize data fluctuations. Dot-dash lines, in particular, are excellent for highlighting key data points within a broader trend. The choice of line style directly influences how the audience perceives and interprets the presented data.
Comparing Datasets with Dot-Dash Lines
To effectively compare two datasets, a dot-dash line style can be used to represent one dataset while a solid line represents the other. This approach clearly distinguishes the two datasets visually, enabling a direct comparison of their trends. For instance, in a scientific study comparing two different treatment groups, dot-dash lines could highlight the treatment group A data points, and a solid line could represent the control group data.
This visualization method provides a clear way to analyze and interpret the differences between the two groups.
Distinguishing Multiple Dot-Dash Lines
Distinguishing between multiple dot-dash lines is essential for clarity in a plot containing multiple datasets. The key is using varying dash patterns or line colors. For example, one could use a short dot-dash pattern for one dataset and a longer dot-dash pattern for another, or different colors. This ensures each dataset maintains its unique visual identity, preventing confusion when comparing multiple trends.
A legend is also a helpful tool to clearly identify each line style.
Examples in Different Contexts
Dot-dash lines can be used in various contexts to enhance data comprehension. In scientific reports, dot-dash lines can be employed to highlight experimental data points, aiding the reader in understanding the results of a study. In engineering applications, these lines can be used to depict a target value against the measured data, allowing engineers to assess the deviation from the target.
Illustrative Plots Enhancing Data Comprehension
Consider a scenario where a company wants to track its sales performance over the past year. They have two product lines: “Product A” and “Product B.” Using dot-dash lines for “Product A” and solid lines for “Product B,” a plot could visually represent the sales trend for each product. This method allows for an easy comparison of sales growth between the two products.
Another example: in an environmental study comparing carbon dioxide levels over time in two different regions, dot-dash lines for region A and dashed lines for region B can effectively show the differences and trends.A table summarizing these approaches can be beneficial:
| Dataset | Line Style | Color |
|---|---|---|
| Product A | Dot-dash | Blue |
| Product B | Solid | Red |
These examples showcase how dot-dash lines, when used strategically, can significantly enhance the clarity and comprehension of data presented in a plot.
Advanced Dot-Dash Line Plot Customization
Taking dot-dash line plots beyond the basics opens up a world of customization options for enhancing data visualization. By manipulating plot properties, we can significantly improve the clarity and impact of our visualizations. This allows for a more nuanced understanding of the underlying data trends.
Controlling Line Appearance with Plot Properties
MATLAB’s plotting functions provide a wealth of properties that enable precise control over the appearance of dot-dash lines. These properties allow us to adjust the line width, color, and marker style to create plots that effectively communicate the data’s key features. Understanding and utilizing these properties is essential for creating professional-grade visualizations.
Modifying Line Width, Color, and Marker Size
The LineWidth property dictates the thickness of the line, while the Color property determines the line’s hue. Adjusting these properties can highlight specific data series or emphasize critical trends. For example, a thicker red line might be used to represent a crucial metric, making it stand out from other less important data points. Similarly, using marker size can further highlight important data points.
The MarkerSize property controls the dimensions of the markers.
Example: To plot a line with a width of 2 pixels and a color of ‘red’, use the following code:
plot(x, y, '.-', 'LineWidth', 2, 'Color', 'red');
Incorporating Line Markers
Line markers, such as circles, squares, or stars, can be added to dot-dash lines to emphasize data points or provide additional visual cues. The Marker property controls the shape of the markers. The MarkerSize property, as mentioned previously, adjusts the size of these markers.
Example: Plotting a line with circles as markers and a specific size can enhance the visual representation:
plot(x, y, '.-o', 'LineWidth', 2, 'Color', 'blue', 'MarkerSize', 8);
Specifying Dash Patterns
The LineStyle property allows us to precisely define the dash pattern. This is especially useful for distinguishing multiple lines on a single plot or highlighting specific patterns in the data. The LineStyle can be a string containing characters for different line styles. The dash pattern is specified by an array of numbers, such as [5 2], where the numbers represent the length of the dash and the length of the space between dashes.
Example: To create a line with a dash pattern of 5 units dash, 2 units space, and a red color, use:
plot(x, y, '.-', 'LineWidth', 2, 'Color', 'red', 'LineStyle', '-.');
Illustrative Examples of Customizations
Here are a few examples showcasing diverse combinations of dot-dash line customizations. These examples demonstrate the practical application of the properties discussed above.
- A thick, blue dot-dash line with large circles as markers can effectively highlight a significant trend.
- A thin, green dashed line with small squares as markers can be used for secondary data.
- A combination of different dash patterns allows for easy comparison of multiple data sets.
Customization Options Summary Table
| Line Style | Line Width | Color | Marker Size | Dash Pattern |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| .- | 2 | ‘red’ | 10 | [5 2] |
| — | 1 | ‘blue’ | 6 | [10 5] |
| -. | 1.5 | ‘green’ | 8 | [3 1] |
Dot-Dash Lines with Multiple Datasets
Plotting multiple datasets on the same graph is a common practice in data visualization. Using distinct dot-dash line styles for each dataset enhances clarity and allows for easy comparison of trends and patterns. This approach is especially useful when analyzing different groups or conditions within a single experiment or study. This section dives into the techniques for creating compelling and informative visualizations with multiple dot-dash lines.Creating well-organized plots with multiple dot-dash lines involves careful consideration of line styles, legend placement, and plot layout.
Clear distinctions between datasets are crucial for avoiding confusion and enabling insightful interpretation of the data. Proper use of legends and consistent line styles throughout the plot will lead to a more professional and easily understandable visualization.
Plotting Multiple Datasets
To effectively display multiple datasets using dot-dash lines, we need to assign unique dot-dash line styles to each data series. This allows for visual differentiation and facilitates the identification of trends for each dataset. For example, if we are plotting sales data for two different product categories, one dataset could be represented by a red dot-dash line, while the other could be represented by a blue dot-dash line.
Using Legends for Distinction
Legends are essential for clarifying the meaning of different lines in a plot with multiple datasets. They provide a key to identify each dataset, particularly when using multiple dot-dash line styles. The legend should accurately reflect the data it represents, and should be easily accessible and not obstruct the visualization of the plot. For example, a legend entry for the red dot-dash line might be labeled “Product A Sales,” while the blue dot-dash line might be labeled “Product B Sales.”
Dot-dash line plotting in MATLAB is a cool way to visualize data, but sometimes it’s tough to get the exact look you want. Speaking of confidence, Lakers’ D’Angelo Russell’s 21-point performance, where he famously declared “I believe in myself more than anybody,” demonstrates a similar level of control over the game. It’s like that same confidence you need to precisely customize your dot-dash line plots in MATLAB.
You just need to know the right commands to get the perfect style.
Comparing Line Styles for Different Datasets
Different line styles can be used to distinguish datasets effectively. Beyond just color, the use of dot-dash lines, dashed lines, solid lines, or other combinations can make the visualization even more clear and comprehensive. For example, plotting a dataset representing the temperature with a red solid line, and another dataset representing the humidity with a blue dashed line will enhance the clarity of the plot and ease the interpretation of the results.
Best Practices for Clear Plots
Maintaining a consistent visual theme is crucial for plots with multiple dot-dash lines. This includes choosing appropriate colors, line styles, and markers. Using a consistent legend placement and ensuring adequate space for labels and titles will contribute to a clear and understandable visualization. The labels should be clear and concise, and avoid ambiguity. The titles should summarize the content of the plot.
Adjusting Plot Layout
The plot layout should be optimized to maximize clarity and minimize clutter. Avoid overcrowding the plot with too many elements. Adjusting the position of the legend, the size of the plot elements, and the overall spacing can significantly impact the overall clarity of the plot. Proper placement of the legend, axis labels, and titles, and ensuring sufficient spacing between data points and plot elements are vital for clarity and comprehension.
Grouping Data
Grouping data points with the same characteristics can further improve the clarity of plots with multiple dot-dash lines. For instance, if the datasets represent sales data for different quarters, the data points for each quarter can be grouped together using different shades of the same color or different line styles. This visually highlights the relationships between different data points, facilitating an easier comprehension of the data patterns.
This could involve using different shades of a color for different quarters, creating a clear visual distinction for each group of data.
Dot-Dash Lines and Subplots: Dot Dash Line Matlab
Mastering the art of visualization in MATLAB often involves presenting data in a clear and organized manner. Subplots provide a powerful tool for comparing different datasets or aspects of a single dataset side-by-side. Combining subplots with the distinctive dot-dash line style enhances the visual appeal and facilitates quick comprehension of the underlying trends. This section delves into techniques for effectively incorporating dot-dash lines into MATLAB subplots, along with customization options for a professional presentation.Creating visually compelling subplots is crucial for effective data communication.
By strategically using dot-dash lines with varied appearances and layouts, analysts can enhance the clarity and impact of their findings. The ability to customize the look of dot-dash lines within each subplot, combined with the arrangement of multiple subplots, offers a highly flexible way to display complex information in a concise and easily digestible format.
Controlling Dot-Dash Line Appearance in Subplots
Customizing the appearance of dot-dash lines within each subplot allows for targeted emphasis of specific data points. Different line widths, colors, and marker styles can be used to highlight particular trends or comparisons. For example, a thicker dot-dash line in one subplot might emphasize a crucial metric, while a thinner line in another subplot might be used for a supporting dataset.
Creating Layouts with Multiple Subplots
MATLAB’s subplot function provides a versatile mechanism for arranging multiple plots into a grid structure. This grid structure is particularly beneficial when examining relationships between variables across different conditions or time periods.
Examples of Subplots with Multiple Dot-Dash Lines and Different Customizations
To illustrate, consider an example comparing the performance of two algorithms (Algorithm A and Algorithm B) across various input sizes. Subplots can be used to showcase the time taken by each algorithm to complete tasks for different sizes. One subplot could display the execution time of Algorithm A with a blue dot-dash line, while the second subplot displays the execution time of Algorithm B using a red dot-dash line.
To further enhance the clarity, the dot-dash lines could have different marker styles (e.g., circles for Algorithm A and squares for Algorithm B) and varying line widths.Using the `subplot` function in MATLAB, we can efficiently create such a visual layout. For example:“`matlabfigure;subplot(2,1,1); % Creates a 2×1 grid of subplots, and selects the first oneplot(x, y1, ‘–.b’, ‘LineWidth’, 2); % Plot data y1 with blue dot-dash line, thickertitle(‘Algorithm A’);xlabel(‘Input Size’);ylabel(‘Execution Time’);subplot(2,1,2); % Selects the second subplotplot(x, y2, ‘–rs’, ‘LineWidth’, 1.5); % Plot data y2 with red dot-dash line, thinnertitle(‘Algorithm B’);xlabel(‘Input Size’);ylabel(‘Execution Time’);“`This code snippet creates two subplots, each displaying the execution time of an algorithm.
The dot-dash lines are customized with different colors, line widths, and marker styles, enhancing visual clarity.
Organizing Subplots with Corresponding Dot-Dash Line Styles
A key aspect of effective subplot design is maintaining a consistent and logical visual representation. The dot-dash line styles, colors, and markers should align with the data they represent, making it easy to distinguish different datasets.
Dot-Dash Lines for Specific Applications
Dot-dash lines, with their distinctive visual pattern, offer more than just aesthetic appeal in MATLAB plots. They serve as powerful tools for enhancing the clarity and interpretability of data within various fields. By strategically employing these lines, researchers and engineers can highlight key trends, differentiate multiple signals, and present complex information in a more accessible format. This section delves into practical applications of dot-dash lines, demonstrating their value in diverse fields.Dot-dash lines excel at visually distinguishing data sets, making plots easier to read and understand, especially when dealing with numerous overlapping signals or experimental results.
This visual separation allows for a clearer identification of patterns and anomalies within the data. This is particularly useful in areas where identifying nuances is crucial.
Signal Processing Applications
Dot-dash lines prove invaluable in signal processing, enabling the isolation and visualization of distinct signal components. For example, consider a signal comprised of multiple superimposed waves. By plotting each component with a unique dot-dash pattern, researchers can visually distinguish and analyze each wave’s characteristics.
| Application | Description | Example Plot |
|---|---|---|
| Signal Processing | Visualizing signal components | A plot showing a complex signal (e.g., a combination of sine waves) where each constituent sine wave is plotted with a distinct dot-dash line pattern. The x-axis represents time, and the y-axis represents the signal amplitude. The plot would clearly illustrate how the different sine waves contribute to the overall signal, with each wave’s dot-dash line highlighting its unique frequency and phase. |
Control Systems Applications
In control systems analysis, dot-dash lines can effectively illustrate the response of a system to different input signals or varying parameters. Plotting the system’s output with different control strategies using distinct dot-dash lines allows for direct comparison of performance metrics. For example, comparing the step response of a system under different PID controller configurations can be visually depicted by using various dot-dash patterns for each configuration.
This visual comparison aids in selecting the optimal control strategy.
Scientific Research Applications
Within scientific research, the use of dot-dash lines enhances the presentation of data analysis and modeling results. For example, when comparing experimental data with theoretical models, distinct dot-dash lines can differentiate between the two datasets, making it straightforward to identify discrepancies or areas requiring further investigation. Further, when multiple datasets are included in a plot, the use of dot-dash lines can significantly enhance the clarity of the data presentation, allowing for a better understanding of the underlying trends and relationships between the variables.
Creating Plots for Specific Trends
To highlight specific trends or patterns, the dot-dash line can be combined with other plot elements, such as different colors, markers, and annotations. For example, when investigating the impact of temperature on a chemical reaction, a plot could use a red dot-dash line to represent the reaction rate at a high temperature and a blue dot-dash line to represent the reaction rate at a low temperature.
These distinctions allow researchers to easily track and understand the trend of reaction rates with varying temperatures.
Last Word
In conclusion, mastering dot-dash line MATLAB plots allows you to create visually appealing and informative visualizations. We’ve covered the fundamentals, customization options, and practical applications. From enhancing data comprehension to producing professional-quality plots for reports and presentations, dot-dash lines are a valuable tool in your MATLAB toolkit. Experiment with the techniques demonstrated here to tailor your plots to specific needs and effectively communicate your data.